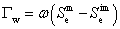Water Flow Equation
Richards' equation for variable-saturated water flow [Simunek and van Genuchten, 2008]
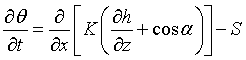
|
θ |
water content |
|
t |
time [T] |
|
x |
spatial coordinate [L] |
|
h |
pressure head [L] |
|
K |
unsaturated hydraulic conductivity [L/T] |
|
α |
angle between flow direction and the vertical axis [°] |
|
S |
sink term [L3/L3T] |
Dual porosity model for variable-saturated water flow [Simunek and van Genuchten, 2008]
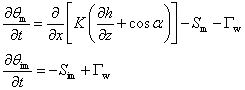
|
θm |
water content of mobile region |
|
θim |
water content of immobile region |
|
t |
time [T] |
|
x |
spatial coordinate [L] |
|
h |
pressure head [L] |
|
K |
unsaturated hydraulic conductivity [L/T] |
|
α |
angle between flow direction and the vertical axis [°] |
|
Sm |
sink term of mobile region [L3/L3T] |
|
S |
sink term of immobile region [L3/L3T] |
|
Γw |
water transfer term between mobile and immobile region [M/L3T] |
The water transfer term can be expressed in terms of fluid saturation or pressure head differences [Simunek et al., 2003]. The expression in terms of fluid saturation is given by:
|
ω |
first-order rate coefficients [T-1] |
|
Sem |
effective fluid saturation of mobile region |
|
Sem |
effective fluid saturation of immobile region |
The effective fluid saturations for the mobile and immobile regions need the saturated and residual water content of the mobile and the immobile region, respectively.