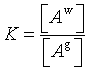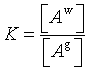|
Equivalence between gas solubility in HPx and HYDRUS
The equilibrium reaction between a single gas and aqueous component:
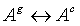
where Ag and Aa are the names of the gas component and the aqueous component, respectively. The mass law action equation for this equation is:
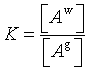
where [] denotes activity and K is the mass action constant. For the case where the activity correction coefficient is 1 and for a gas component at low gas pressures, the mass law action equation becomes:
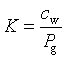
where Pg is the partial pressure of Ag [atm].Using the ideal gas low (PV=nRT ; P=(n/V)RT), the equation can be written as:
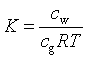
where n is the number of moles of the gas component, V is the gas volume, T is temperature [K], and R is the universal gas constant (=0.0.82057 L atm / K mol). This equation shows the equivalence between K and kg [-], the empirical gas constant used in HYDRUS:
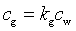
|